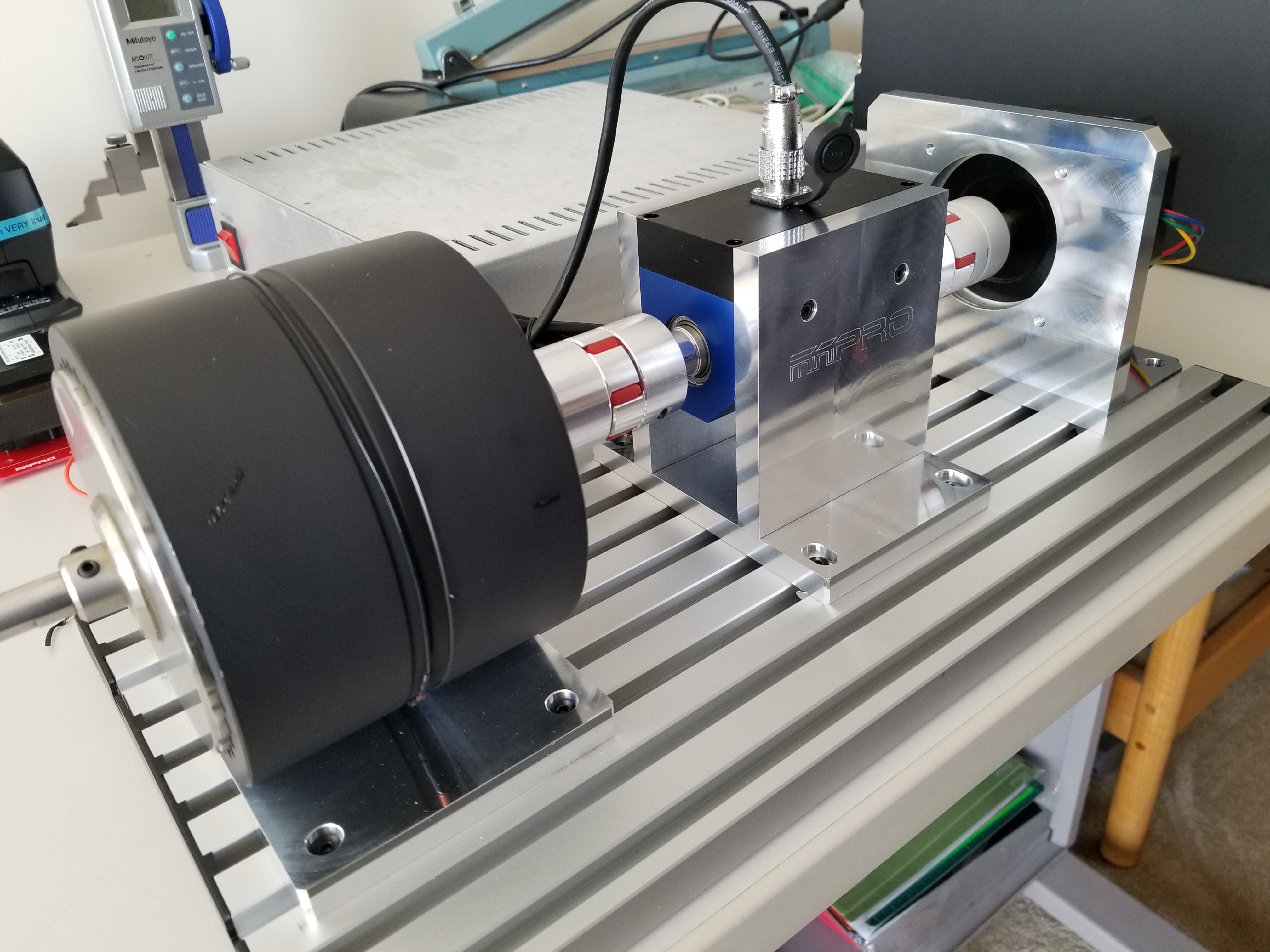
What is an Inertia Dyno?
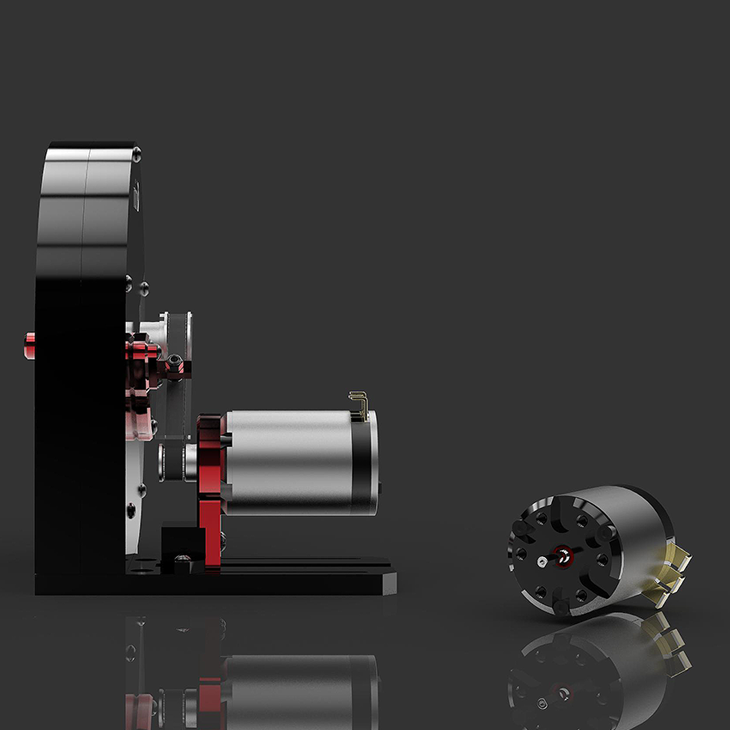
Inertia dynamometers (dynos) are devices used to measure the power output of engines or motors. They work by measuring the rotational speed of a rotating mass, which is attached to the engine or motor being tested. The mass is accelerated by the engine, and the dynamometer measures the torque required to accelerate the mass. From this measurement, the power output of the engine can be calculated.
Inertia dynamometers typically consist of a heavy flywheel, which is attached to the engine or motor being tested. The flywheel is accelerated by the engine, and the torque required to accelerate the flywheel is measured by the dynamometer. The rotational speed of the flywheel is also measured, which allows the power output of the engine to be calculated.
There are several advantages to using inertia dynamometers. They are relatively simple and inexpensive compared to other types of dynamometers. They also have a wide range of applications, and can be used to test engines and motors of various sizes and types. Inertia dynamometers are also relatively easy to operate, and require minimal maintenance.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using inertia dynamometers. They do not provide a load on the engine or motor being tested, which means that they cannot simulate real-world conditions. This can lead to inaccurate results, especially if the engine or motor is being tested under conditions that are significantly different from those in which it will be used.
Additionally, inertia dynamometers are not suitable for measuring transient conditions, such as acceleration or deceleration. They are designed to measure steady-state conditions, and may not be able to accurately measure the power output of an engine or motor during dynamic events.
In conclusion, inertia dynamometers are useful devices for measuring the power output of engines and motors. They are relatively simple and inexpensive, and have a wide range of applications. However, they are not suitable for simulating real-world conditions or measuring transient events, and may not provide accurate results under these conditions. As with any testing equipment, it is important to use the appropriate type of dynamometer for the specific application, and to interpret the results with caution.